Introduction
Vitamin D Deficiency: Hidden Symptoms and How to Fix Them
Vitamin D deficiency is an increasingly recognized global health issue, affecting a significant portion of the population worldwide. It is estimated that nearly 42% of adults in the United States and approximately one billion people globally have low levels of vitamin D. This deficiency varies considerably by geography, being more prevalent in regions further from the equator, such as northern Europe, Canada, and northern states in the U.S., where sun exposure is less intense and less frequent, particularly during winter months.
Why is Vitamin D Important?
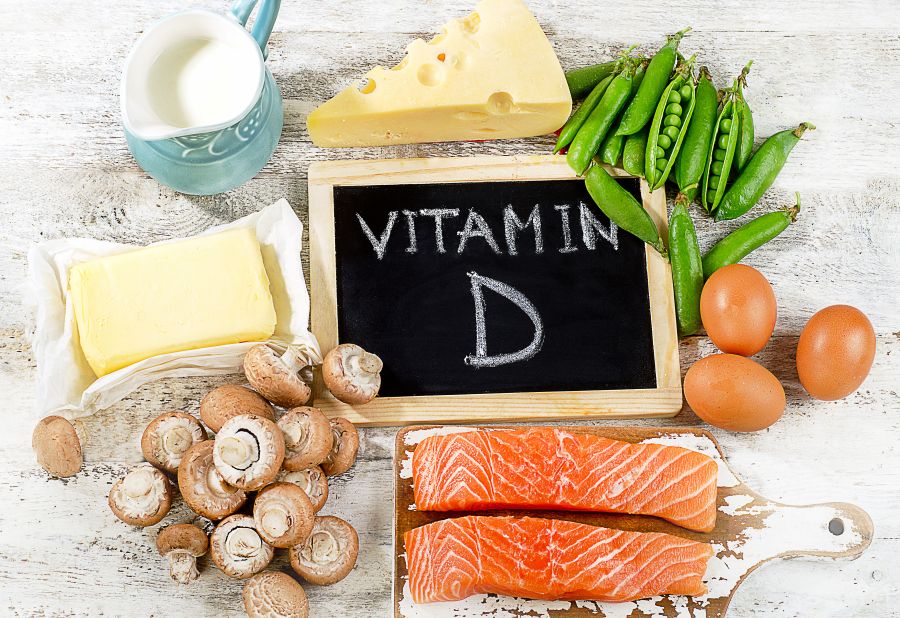
Vitamin D, commonly known as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It aids in calcium absorption, which is essential for strong bones and teeth, supports immune function, helps regulate mood, reduces inflammation, and even impacts cardiovascular and neurological health. Vitamin D is involved in gene expression, affecting numerous bodily functions at a cellular level.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Recognizing symptoms of vitamin D deficiency is crucial, though many are often subtle and easily overlooked. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
1. Fatigue and Tiredness
Persistent fatigue, even after adequate rest, is one of the most frequent complaints of those deficient in vitamin D.
2. Bone Pain and Muscle Weakness
Vitamin D deficiency can cause generalized bone pain, aches, and muscle weakness. Muscle cramps and unexplained muscle pains are typical indicators.
3. Depression and Mood Swings
There is increasing evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to mood disorders like depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and anxiety. Vitamin D receptors are found in areas of the brain associated with mood regulation.
4. Frequent Illness or Infections
Vitamin D is critical for immune function, and a deficiency can make individuals more susceptible to frequent colds, flu, and other infections.
5. Slow Healing of Wounds
Vitamin D aids in wound healing. A deficiency can impair this process, leading to slower recovery from injuries and surgeries.
Less Common but Important Symptoms
While the symptoms above are relatively well-known, several lesser-known symptoms can also signal vitamin D deficiency:
1. Hair Loss
Though often attributed to stress or genetics, unexplained hair loss or thinning hair can also result from inadequate vitamin D.
2. Dizziness and Balance Issues
Research suggests low vitamin D levels may contribute to dizziness, balance problems, and increased risk of falls, particularly in older adults.
3. Cognitive Impairment
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to cognitive decline, impaired memory, and decreased concentration, particularly in older populations.
4. Unexplained Weight Gain
Low vitamin D levels may impact metabolism and fat storage, potentially leading to unexplained weight gain.
How to Supplement Vitamin D: Are Certain Formulations Better?
If you suspect you have low vitamin D levels, the first step is to confirm with a blood test (25-hydroxy vitamin D test). The optimal level is typically considered between 30-50 ng/mL.
Once deficiency is confirmed, supplementation is usually recommended. Vitamin D is available in two primary forms:
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol): The most effective and commonly recommended form, derived from animal sources, including lanolin from sheep’s wool. It has better bioavailability and is more effective at raising vitamin D levels.
- Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol): Derived from plant sources or yeast, this form is less efficient and often requires higher or more frequent doses to achieve similar benefits.
Most health authorities recommend vitamin D3 supplementation due to its higher efficacy.
Recommended Dosage:
Typical daily supplementation ranges from 800-2,000 IU/day for adults. For those severely deficient, doses can range from 4,000 to 10,000 IU/day under medical supervision, with regular monitoring to avoid toxicity.
Osteoporosis and Other At-Risk Populations
Certain populations are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency and related complications:
1. Individuals with Osteoporosis or Low Bone Density:
Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption and bone density maintenance. Individuals with osteoporosis or at high risk should ensure optimal vitamin D levels to prevent further bone loss and fractures.
2. Elderly Adults:
Aging decreases skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. Older adults are particularly vulnerable to deficiency, leading to increased fracture risk and compromised immune function.
3. People with Darker Skin:
Higher melanin levels reduce the skin’s ability to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight, increasing deficiency risk among individuals with darker skin tones.
4. Those with Limited Sun Exposure:
People who spend significant time indoors, those who consistently use sunscreen, or individuals living in northern latitudes have limited exposure to UVB rays needed for vitamin D production.
5. Individuals with Malabsorption Disorders:
Conditions such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, or gastric bypass surgery impair vitamin D absorption, significantly increasing deficiency risk.
Should Everyone Take Vitamin D?
While vitamin D supplementation has clear benefits for deficient individuals, universal supplementation remains debated. For most healthy adults who spend ample time outdoors and have balanced diets, routine supplementation might be unnecessary.
However, widespread prevalence of deficiency suggests many could benefit from routine supplementation, particularly during winter months, or for those living at higher latitudes.
Healthcare professionals generally recommend:
- Regular screenings for individuals at risk.
- Targeted supplementation based on blood test results.
- Moderate supplementation (800-1,000 IU/day) during winter months in regions with limited sunlight.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread, with subtle symptoms often overlooked. Recognizing the signs—both common and uncommon—and understanding the critical roles vitamin D plays in health is crucial. Targeted supplementation, particularly with vitamin D3, provides an effective solution for deficiency. While not everyone needs routine supplementation, many individuals, especially at-risk populations, should consider regular vitamin D monitoring and supplementation to maintain optimal health.

This article reviewed by Dr. Jim Liu, MD.
There’s nothing more important than our good health – that’s our principal capital asset.
#medical #telehealth #umedoc #vitamin D